Jim Gerhart, May 2021
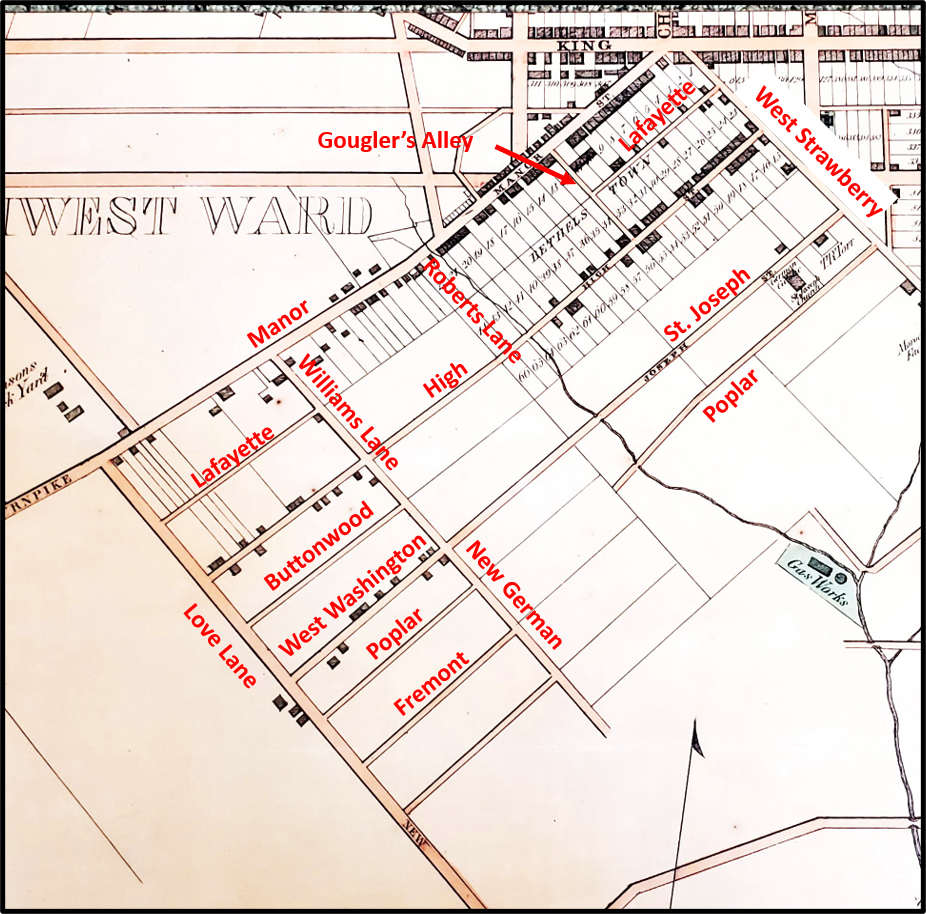
Cabbage Hill was nothing but forest, farmland, and pasture until 1762 when Bethelstown was laid out with 66 building lots on the first two blocks of what would become Manor and High Streets. Bethelstown grew slowly; by 1815, more than 50 years after its founding, there were only about 25-30 houses on its 66 lots. Nearly all of the houses were one-story houses made of logs and rough-sawn wood.
Most of the original houses on Manor and High were later replaced by two- and three-story brick houses built in the second half of the nineteenth century. However, at least one of the charter-member houses of old Bethelstown lasted well into the twentieth century before being razed—a log house with weatherboarding that used to stand at 442 Manor before it was taken down in 1963 to make room for a parking lot.
Which raises the question: Was 442 Manor the only survivor of the original 25-30 one-story houses from old Bethelstown, or is it possible that more of the original one-story houses are still present, hiding behind modern vinyl siding and form-stone? Most of the historical sources needed to answer this question are available online. The only one not completely online is county tax lists, and the staff of LancasterHistory was kind enough to supply the lists for the years not yet online.
Using Google Maps, I was surprised to discover that 27 one-story houses are still present in the 400 and 500 blocks of Manor and High. Of the 27, nine are single houses, fourteen are in seven house pairs, and four are grouped together in a connected row of houses. Using newspaper articles, city directories, street maps, property deeds, and other sources, I was able to determine that 20 of the 27 current one-story houses in the first two blocks of Manor and High were built in 1850 or later, and therefore are not old enough to be original houses from old Bethelstown. The remaining seven possibilities—two on Manor and five on High—were investigated in more detail.

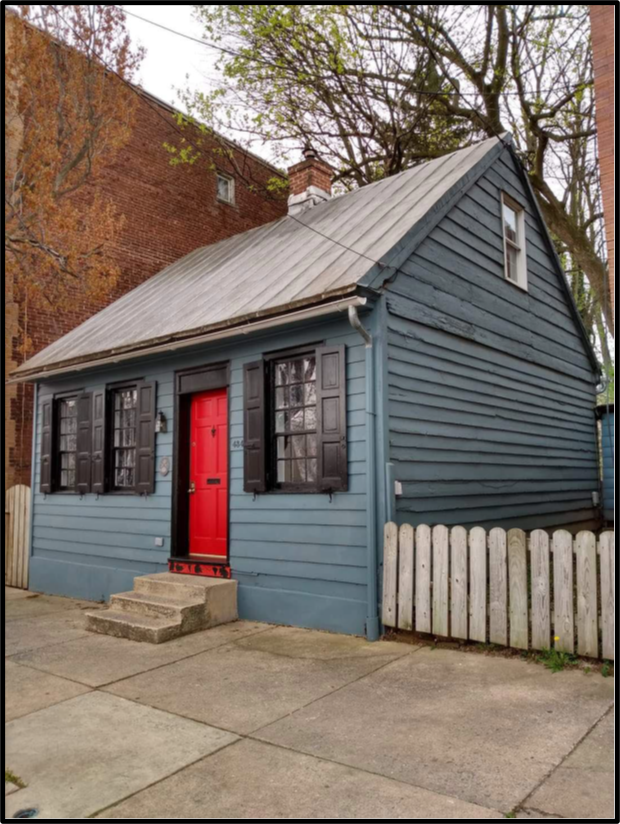
frame house at 435 High (left). Author’s photo, 2021.
Of the seven houses that predate 1850, five were found to have been built in the 1840s, leaving just two—433 and 435 High Street—that had the potential to be old enough to be original Bethelstown houses. A couple of key deeds and tax records show that these two one-story houses, which are next-door neighbors on the northwest side of the 400 block of High, were built on Bethelstown lot 28, and that both houses were already present in 1840. The deeds show that 433 is a log house, adding to the potential that it could have been built quite a bit before 1840.
Making things a little more challenging, detailed maps and city directories do not exist before 1840, and many pre-1840 deeds that would be helpful seem to have gone unrecorded or have been lost. Consequently, tax lists took on a more important role in tracking these two houses before 1840. The continuity from year to year in the amount of ground rent paid for the lot, as well as the assessed value of the houses, enabled me to trace 433 and 435 High back in time before 1840 with some success. Also helpful were occasional notes written by the tax assessor when the properties were bought or sold.[1]
The result is that “YES” is my answer to the question of whether any of the 25-30 houses from the pre-1815 days of old Bethelstown have survived. The weight of the evidence points to the one-story log house at 433 High as the oldest surviving house on the Hill. It appears to have been built no later than about 1801, and possibly earlier. Not surprisingly, because they are neighboring houses on the same original lot, the one-story frame house at 435 High also is old, having been built about 1814. I believe these two are the oldest surviving houses on Cabbage Hill—older by at least a couple decades than Catharine Yeates’ 1838 summer cottage at 613 Fremont, previously considered the oldest survivor.

So, who built these historic houses at 433 and 435 High, and who were their early owners? The early history of the houses involves a couple generations of the Bier family. Peter Bier, Sr. (1701-1781) was a German immigrant who arrived in this country in 1748, bringing with him a teenaged son, Peter, Jr. (1732-1801), and settling in Lancaster about 1760. Peter, Jr. was a cordwainer (shoemaker) living in the southeast part of the city, but owning several other houses and significant acreage, including on the Hill. Peter, Jr. married Elizabeth Buch in 1760 at First Reformed Church, and they had a son, Peter III (1763-1843). Peter III also was a shoemaker, but later in life a farmer. Peter III and his wife Catharine had several children, including a fourth-generation Peter (1797-1849) who became a doctor.
Peter Bier, Jr., who died in 1801, appears to have acquired Bethelstown lot 28 shortly before his death. Peter, Jr. may have built the house now at 433 High as soon as he acquired the lot, or the lot may have already had the house on it when he acquired it. If Peter, Jr. built it, the house dates to about 1800-01; if lot 28 already had a house on it when he bought it, the house dates to the late 1700s and was built by an unknown first owner. I suspect the house was already there when Peter, Jr. bought the lot, because he died within six months, and probably would not have had the time to build a house. This means the house likely was built in the late 1700s.
As part of Peter, Jr.’s estate, lot 28 and the house on it was inherited by his widow Elizabeth. She may have lived in the house for a short time, but mostly she rented the house to a series of tenants, including, in the years immediately following Peter, Jr.’s death, to John Williams, a young mason who decades later would end up owning most of the land in the southern half of Cabbage Hill. Also, a few records suggest that John Drepperd may have lived in the house in the early 1810s. Drepperd was a gunmaker whose father and grandfather were both famous gunmakers supplying rifles for troops in the Revolutionary War.
Sometime about 1814, the widow Bier (or her son Peter III) seems to have added a frame house to lot 28 (now 435 High). Both houses were occupied by tenants for the next 10 years or so, but then, about 1824, Elizabeth transferred the deed for the lot and houses to her son Peter III. Peter III continued to rent the houses to tenants up until 1841 when he sold lot 28 and both houses to Jacob Liphart, a real-estate investor who lived in Marietta.
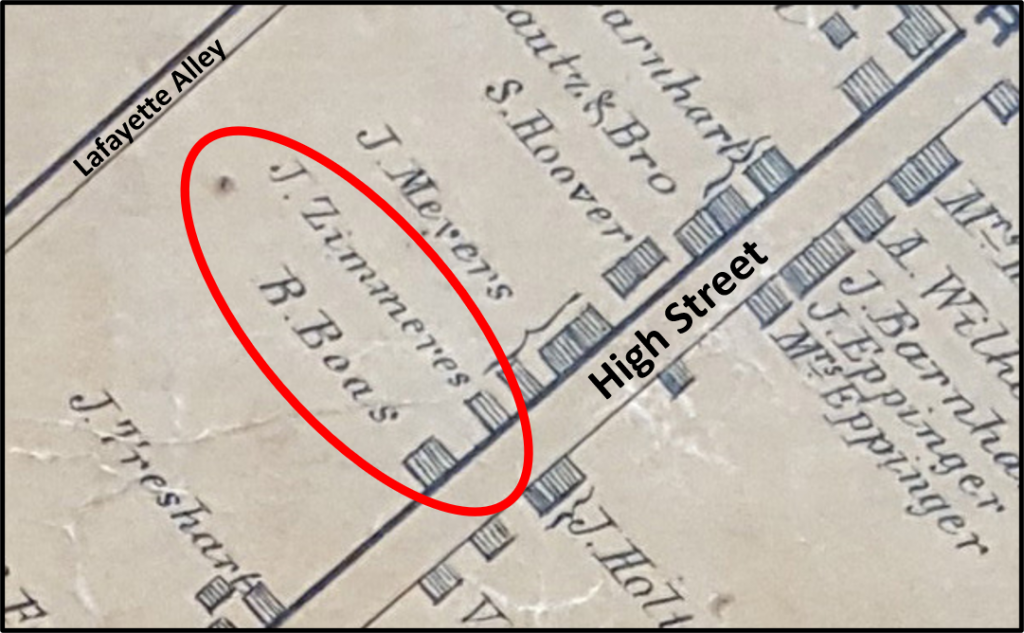
Liphart rented the houses out for a short while, and then split the 62-foot-wide lot in half, with the northeast half containing the one-story log house now numbered 433 High, and the southwest half containing the one-story frame house now numbered 435 High. In 1844, Liphart sold the half with 433 to John Zimmerer, a middle-aged tailor and his wife Sarah. Earlier, in 1842, Liphart had sold the half with 435 to Robert Boas, a middle-aged laborer, his wife Franciska, and their young son. Both Zimmerer and Boas were German immigrants, and both families lived in the houses they had bought, each of which was valued at $220 in 1845.

John Zimmerer died in 1857, and his wife Sarah sold the log house at 433 to Jacob and Susan Glassbrenner for $300. The Glassbrenner family lived in the house for a few years and then rented it out to tenants. After Jacob died, his widow Susan, who had moved to Philadelphia, sold the house to William Lebkicher in 1906.
Robert and Franciska Boas lived in the frame house at 435 High for many years. Sometime in the 1860s, they added the two-story brick house next door at 437 High, squeezing it into the remaining part of their lot. Boas and his wife moved into the larger 437 and rented 435 out to tenants until Boas’s death. In 1881, the frame house at 435 High and its larger brick companion at 437 were sold as part of Boas’s estate for $1,000 to John Kirsch. In 1920, after Kirsch had died, the courts granted the property to his widow Barbara at a value of $500 as part of her widow’s exemption.
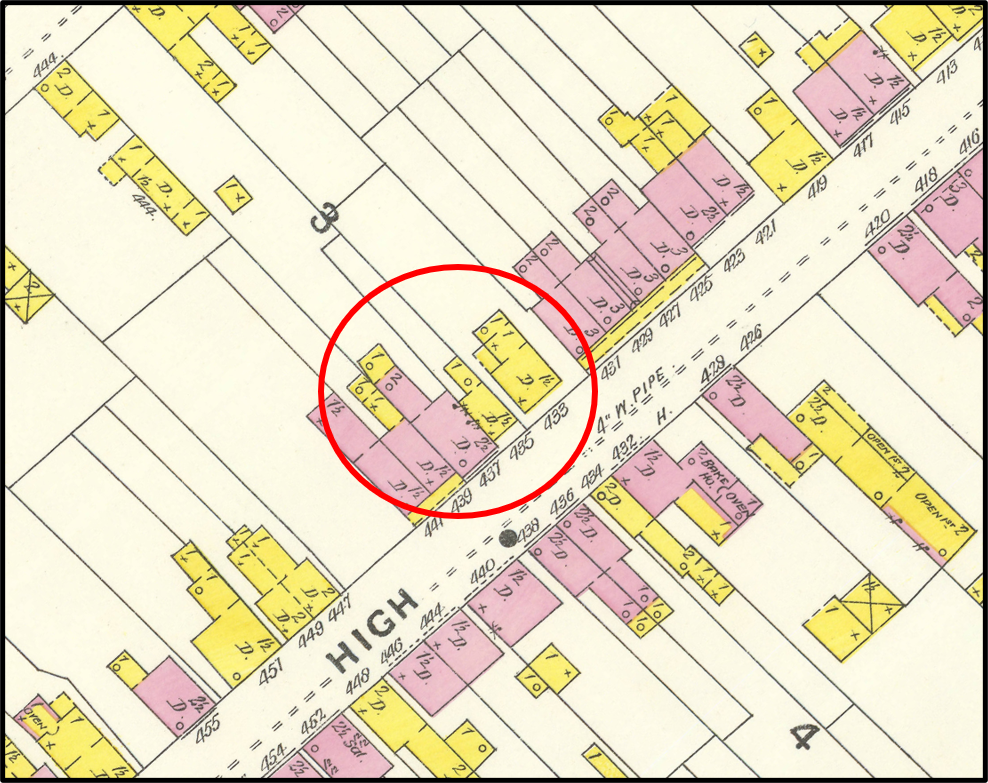
Today, Peter Bier III would have difficulty recognizing his houses. The one-story log house at 433 High is covered with vinyl siding, and the one-story frame house at 435 High is sheathed in gray form-stone. Both houses have had their original doors, windows, and roofs replaced. Dormers have been replaced or enlarged, and concrete steps now lead up to the front doors. But behind all the modern features, more than 200 years of history lie hidden.
It is my belief that 433 and 435 High Street are the only two houses that survive from the original 25-30 houses built in old Bethelstown between 1762 and 1815. Since Bethelstown preceded the development of the rest of the Hill, these two houses also are the oldest surviving houses on all of Cabbage Hill.
Sometimes a little historical sleuthing can uncover some remarkable stories hiding just behind modern siding and form-stone on the old houses on the Hill.